Albert Einstein:
the genius who fast-tracked science
Einstein lived from 1879 to 1955.
He was born in Germany.
“The true sign of intelligence is not knowledge but imagination” – Albert Einstein
You might have seen pictures of Einstein with his wild hair and funny face…who would guess he was one of the smartest scientists ever?
Yet he helped us understand how the universe works — from the smallest bugs to the biggest galaxies.
And you know what? Einstein said that being smart isn’t just about knowing a lot — it’s about asking questions. And using your imagination to find answers.
When he was a kid, it took him longer to say his first words than most children. His parents worried there was something wrong with him.
Later, when he decided to study science, Einstein started out with the same books as every other German scientist.
But he found his own answers little by little…and believed that if you keep trying, you might just discover something amazing!
Einstein’s big discoveries rocked the world
He published more than 300 scientific papers, but his most famous work is his theories of relativity. They explain how time, space, and gravity are connected like a big fabric.
He published them in 2 parts: the Special Theory of Relativity in 1905, and the General Theory of Relativity in 1915.
Let’s explore in four simple chunks how “Everything is relative:”
Time Changes with Speed
Einstein figured out that time can slow down depending on how fast you’re moving.
Imagine you’re traveling in a spaceship really fast — close to the speed of light. Meanwhile, a friend who’s your same age stays on Earth.
Because you’re zooming around so fast, something strange happens with time. For you inside the spaceship, everything seems normal. You eat your space snacks and play your space games, and time ticks by just like it does on Earth.
But when you finally come back from your adventure, you find that your friend is older than you. This is because the faster you move, the slower time goes for you.
Today, this helps our GPS work well. Satellites in space move very fast, and their clocks work differently from those on Earth. Scientists use Einstein’s ideas to correct these differences.
Nothing travels faster than light
Einstein’s studies helped us see how energy and light work.
He discovered that light always travels at the same speed — the fastest speed in the universe.
If you could move as fast as light, you would go around the Earth 7.5 times in one second!
Then, he showed us that light is made of tiny particles called photons. When those photons hit certain materials, they create electricity.
This discovery powered up the invention of cameras, solar panels, lasers, and doctors’ machines.
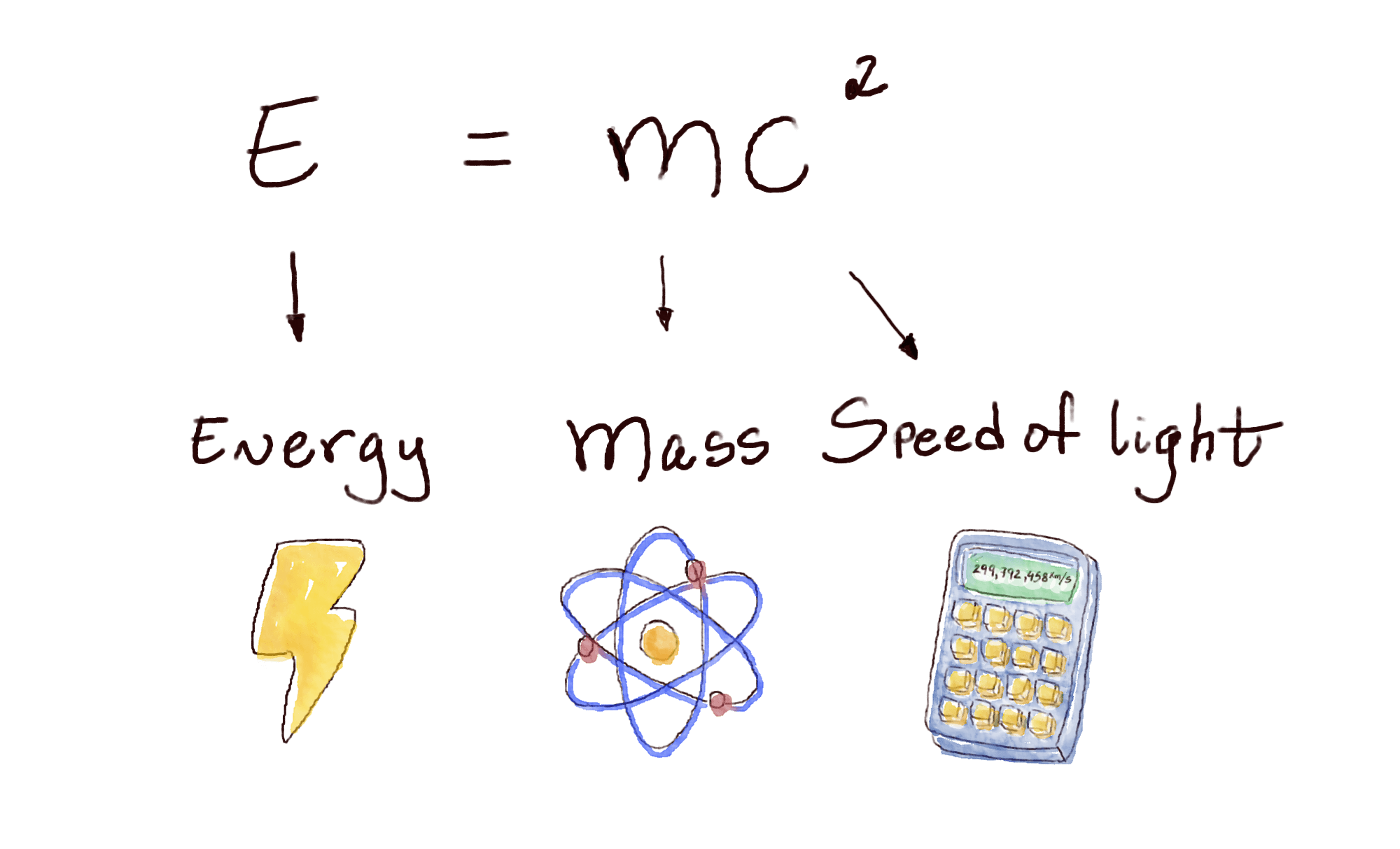
Mass and Energy Are the Same
Einstein proved that you can transform mass into energy and energy into mass. He wrote a formula that shows how they’re connected:
E = mc²
Let’s put it in a way that’s easy to understand:
E: Energy is what makes things go, like cars driving, lights shining, and your body moving.
m: Mass is how much matter, or stuff, something has. For example, you have mass and so does everything around you, like trees and bugs.
c: The speed of light is about 299,792 kilometers per second (or about 186,282 miles per second).
So, energy equals mass times the speed of light squared.
What that means is…
Even a little bit of mass can turn into a lot of energy.
This happens in the Sun, where tiny particles smash together and make huge amounts of energy. And in nuclear reactions, where splitting particles create a huge explosion.
Scientists use this idea in nuclear power houses — they change a tiny bit of mass into a huge amount of energy to give cities and towns electricity.
Einstein felt sad when he saw his equation used to make nuclear bombs, because they destroy things. He had hoped scientists would use his ideas to do good.
How About Turning Energy into Mass?
In space, cosmic rays crash into tiny particles. Sometimes, this makes new particles that join to create things like stars or meteors.
Scientists use special machines that work like this. When they focus a lot of energy in a small place, they can make matter particles.
They study these particles to understand how the universe works, which helps them invent more technology.
Perhaps one day they’ll learn how to join those particles to make things, just like in movies!
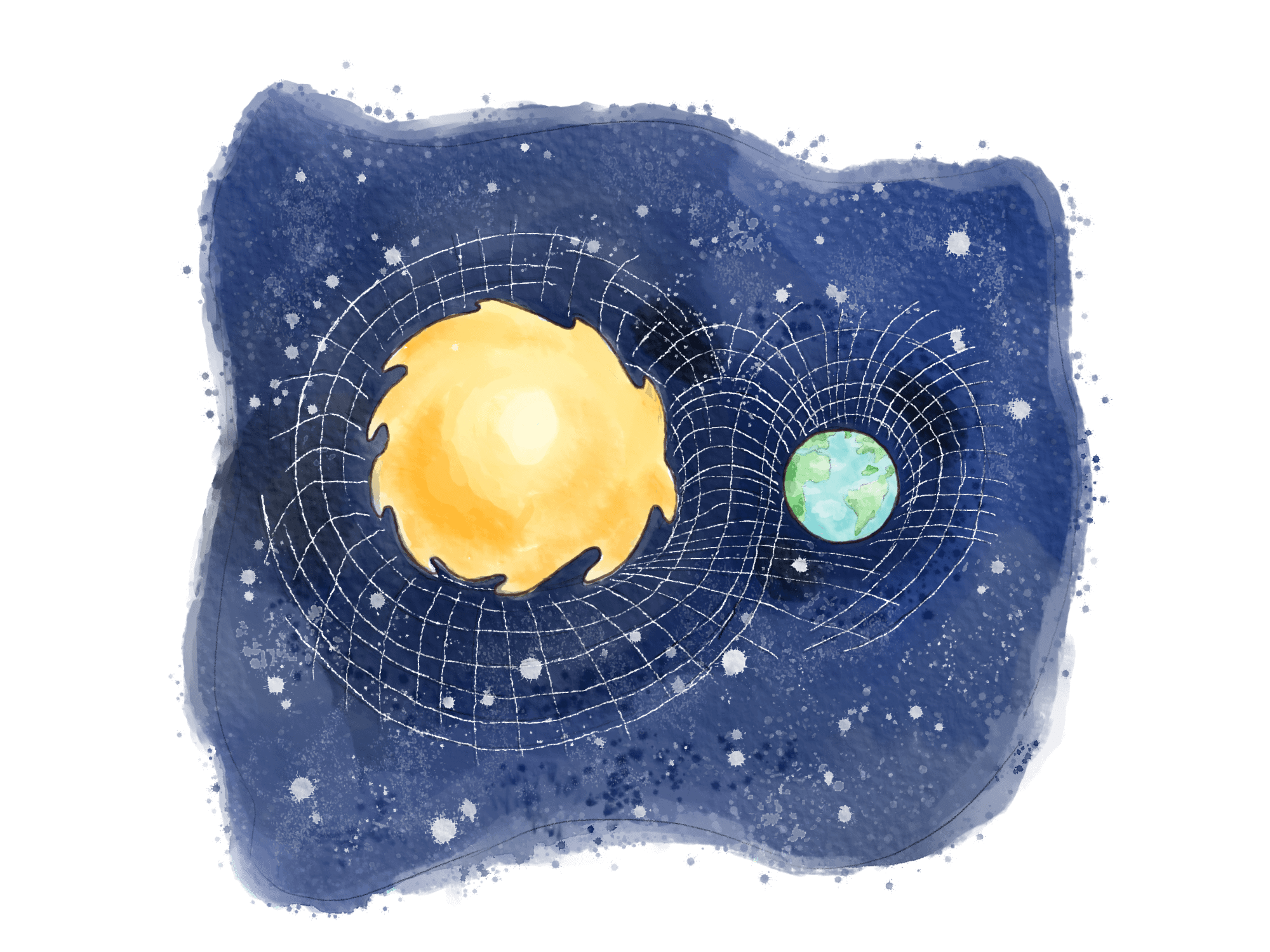
Big Things Affect Spacetime
Einstein figured out that gravity isn’t just a force that pulls things down, like apples falling from trees.
But rather, space and time are like a big fabric. Heavy things like planets and stars make dips in the “spacetime” fabric.
Those dips are what we feel as gravity on Earth.
In Einstein’s time, this idea helped scientists understand how planets orbit the Sun. It turns out, the Sun does not pull planets like a magnet. Instead, the heavy dip from its weight makes planets move in a curved path around it.
Today, astronauts fly their spacecraft and predict how planets will move based on this finding.
Einstein also discovered that when light passes near something really heavy, like stars, it bends — just as water bends around rocks in a stream. That’s because gravity bends light too!
“How Do Planets Follow the Curved Path Instead of Rolling into the Sun?”
Great question! The planets don’t roll straight into the Sun because of their momentum and the way gravity curves space around them.